What is systolic blood pressure?
18/11/2023
Blood pressure is one of the simplest parameters to evaluate human health status. High or low blood pressure will make us tired, uncomfortable and even lead to many dangerous complications. Blood pressure index consists of two components: systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Among them, the systolic blood pressure index often receives the most attention.
1. What is systolic blood pressure?
When measuring blood pressure, especially with electronic devices, we often see two indicators appear: maximum blood pressure - also known as systolic blood pressure, and minimum blood pressure - also known as diastolic blood pressure. . However, not everyone clearly understands what these blood pressure indicators mean.
Systolic blood pressure is the pressure of blood against the arteries when the heart contracts. This number is always of greatest interest, because it represents the heart's ability to pump blood to the organs. Specifically, in each heartbeat, a quantity of blood is ejected from the heart out of the body; the pressure of that blood placed on the artery walls is called systolic blood pressure.
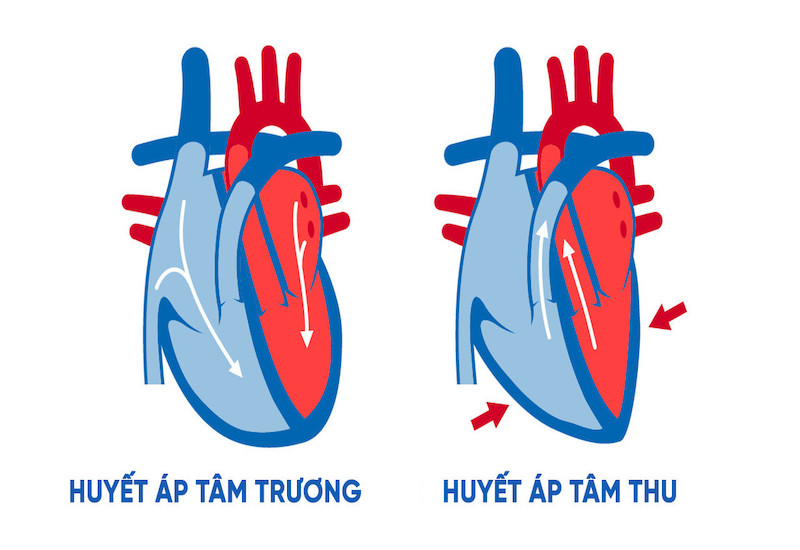
Systolic blood pressure depends on the strength of the heart's contractions and the volume of blood with each beat. The stronger the heart contracts or the more blood ejected, the higher the systolic blood pressure will be and vice versa. When measuring blood pressure with a manual sphygmomanometer, the first heartbeat heard when the air cuff is released marks the systolic blood pressure.
The moment when the last heartbeat is heard before it can no longer be heard is the diastolic blood pressure. This is the blood pressure on the artery walls when the heart relaxes and this number is often paid little attention to, because it only reflects the elasticity of the vessel walls and this factor is difficult to change.
The difference between systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure keeps a certain difference to create perfusion pressure for organs. However, this difference should never be equal to or less than 20 mmHg. If it is below this number, the doctor will determine that this is a case of clamped blood pressure and will perform emergency treatment.
2. What is a normal systolic blood pressure index?
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels are especially important for the effective functioning of vital organs such as the heart, brain and kidneys as well as for general body health. In particular, the meaning of systolic blood pressure is the foundation of blood perfusion for organs to function well.
So what is normal systolic blood pressure? According to the World Health Organization (WHO), normal systolic blood pressure ranges from 90 mmHg to 140 mmHg.
Doctors will diagnose us with hypertension when our systolic blood pressure is 140 mmHg or higher and/or diastolic blood pressure is 90 mmHg or higher.
3. How dangerous is systolic blood pressure disorder?
When systolic blood pressure is kept stable, it reflects stable circulation in the body, blood is regularly pumped by the heart to supply organs. In case systolic blood pressure suddenly increases or drops abnormally, it makes the body uncomfortable and sometimes leads to dangerous diseases.
For sudden increase in systolic blood pressure, the patient will experience severe headaches, neck and shoulder fatigue, fast heartbeat, heavy chest, difficulty breathing, blurred vision... Blood pressure measurement shows a rapid increase in systolic blood pressure. , can be 200 mmHg or more. If not intervened promptly, systolic blood pressure that is too high can damage blood vessels in the brain causing stroke, block blood vessels feeding the heart causing myocardial infarction or respiratory failure due to pulmonary edema, acute kidney failure, Aortic dissection ruptures and can easily lead to death.

As for a sudden drop in systolic blood pressure, the patient will feel tired, physically weak, feel dizzy, dizzy, dizzy, nervous, have a fast heartbeat, and in more severe cases, may feel drowsy. confusion, fainting and loss of consciousness. This is because a sudden drop in systolic blood pressure causes the brain and other organs in the body to not receive enough blood to supply oxygen and nutrients, which can cause cerebral anemia and brain death, which is dangerous. live.
4. How to control systolic blood pressure?
Because high blood pressure or low blood pressure both affect health. Therefore, each person needs to know how to keep blood pressure stable. People with high blood pressure need to comply with their doctor's treatment, take medicine regularly every day and have regular check-ups as scheduled. Along with this, actively building a healthy lifestyle is also extremely necessary.
Among them, diet plays an extremely important role. Encourage eating lots of fiber-rich foods such as brown rice, green vegetables, and ripe fruits. You should not eat fat, animal organs, pre-processed products that contain a lot of salt such as pickled tomatoes, braised dishes, stews, and salty dipping sauces. Quit smoking and limit alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine.

In addition, patients should also exercise regularly and maintain a reasonable weight, which will help maintain good elasticity in the arteries, even in older people, helping to ensure blood flow and blood pressure are at normal levels. Besides, knowing how to relieve stress, relax, meditate, practice yoga and have a good sleep will also help lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of heart disease and death.
Particularly for people with low blood pressure, they should drink more water and eat saltier foods than normal people as well as have more nutrients, enough meals, and a variety of vitamins. Patients should also live in moderation, get enough sleep, and avoid overwork or sudden changes in position. When sleeping, you should keep your head low and your feet high.
Finally, the most important thing to note is to regularly monitor your own and your loved ones' blood pressure to know your health status and intervene promptly to avoid unfortunate consequences that may occur. .
Related posts
[Warning corner] Are post-Covid sequelae dangerous?
18/11/2023
Not only does it affect health during the covid period, SARS-CoV-2 also leaves many sequelae after weeks of recovery. So what sequelae can be encountered? How do you overcome? Let's learn about this issue through the following article.
Treatment methods for heart failure
18/11/2023
Effective treatment of heart failure requires a combination of measures, from changing the patient's diet and lifestyle, treating the causes of heart failure (if possible), and combining medication to reduce symptoms. increase myocardial contractility. In more severe cases, patients also need support devices or heart transplant surgery.
Can ankylosing spondylitis be cured? Treatment
18/11/2023
Ankylosing spondylitis is a chronic bone and joint disease that can seriously affect the patient's daily life. Can the disease be completely cured? Find out how to treat the disease immediately through the following article!
Dangerous effects of alcohol and scary diseases
13/11/2023
Alcohol is a popular drink in parties with friends or customers, but alcohol abuse can lead to many unpredictable harms. Find out immediately about some scary diseases related to alcohol through the following article!



![[Warning corner] Are post-Covid sequelae dangerous?](https://eocvietnam.com/upload/images/bai-viet/hau-covid-1.jpg)